本篇内容主要讲解“Python如何实现数字图像处理染色体计数”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Python如何实现数字图像处理染色体计数”吧!
对于下面这幅图像,编程实现染色体计数,并附简要处理流程说明。
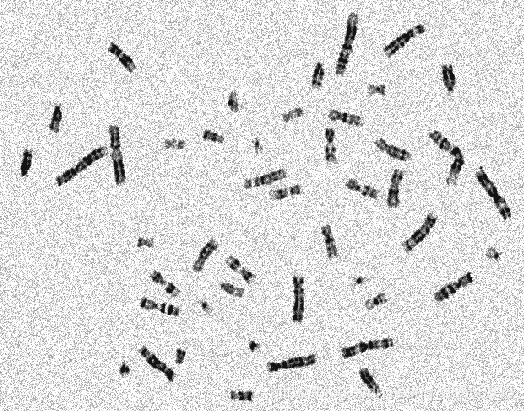

1.中值滤波
2.图像二值化
3.膨胀图像
4.腐蚀图像
5.计算光影背景
6.移除背景
7.检测染色体
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 计算光影背景
def calculateLightPattern(img4):
h, w = img4.shape[0], img4.shape[1]
img5 = cv2.blur(img4, (int(w/3), int(w/3)))
return img5
# 移除背景
def removeLight(img4, img5, method):
if method == 1:
img4_32 = np.float32(img4)
img5_32 = np.float32(img5)
ratio = img4_32 / img5_32
ratio[ratio > 1] = 1
aux = 1 - ratio
# 按比例转换为8bit格式
aux = aux * 255
aux = np.uint8(aux)
else:
aux = img5 - img4
return aux
def ConnectedComponents(aux):
num_objects, labels = cv2.connectedComponents(aux)
if num_objects < 2:
print("connectedComponents未检测到染色体")
return
else:
print("connectedComponents检测到染色体数量为:", num_objects - 1)
output = np.zeros((aux.shape[0], aux.shape[1], 3), np.uint8)
for i in range(1, num_objects):
mask = labels == i
output[:, :, 0][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
output[:, :, 1][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
output[:, :, 2][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
return output
def ConnectedComponentsStats(aux):
num_objects, labels, status, centroids = cv2.connectedComponentsWithStats(aux)
if num_objects < 2:
print("connectedComponentsWithStats未检测到染色体")
return
else:
print("connectedComponentsWithStats检测到染色体数量为:", num_objects - 1)
output = np.zeros((aux.shape[0], aux.shape[1], 3), np.uint8)
for i in range(1, num_objects):
mask = labels == i
output[:, :, 0][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
output[:, :, 1][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
output[:, :, 2][mask] = np.random.randint(0, 255)
return output
def FindContours(aux):
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(aux, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
if len(contours) == 0:
print("findContours未检测到染色体")
return
else:
print("findContours检测到染色体数量为:", len(contours))
output = np.zeros((aux.shape[0], aux.shape[1], 3), np.uint8)
for i in range(len(contours)):
cv2.drawContours(
output,
contours,
i,
(np.random.randint(0, 255),
np.random.randint(0, 255),
np.random.randint(0, 255)), 2)
return output
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('img.png', 0)
pre_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 二值化函数
# 第一步:中值滤波
# 中值滤波
img1 = cv2.medianBlur(img, 3)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('gray', img)
cv2.imshow('medianBlur', img1)
cv2.imwrite('medianBlur.jpg', img1)
# 第二步:图像二值化
# 图像二值化
ret, img2 = cv2.threshold(img1, 140, 255, 0, img1) # 二值化函数
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('threshold', img2)
cv2.imwrite('threshold.jpg', img2)
# 第三步:膨胀图像
dilate_kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
img3 = cv2.dilate(img2, dilate_kernel)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('dilate', img3)
cv2.imwrite('dilate.jpg', img3)
# 第四步:腐蚀图像
erode_kernel = np.ones((7, 7), np.uint8)
img4 = cv2.erode(img3, erode_kernel)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('erode', img4)
cv2.imwrite('erode.jpg', img4)
# 第五步:计算光影背景
img5 = calculateLightPattern(img4)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('LightPattern', img5)
cv2.imwrite('LightPattern.jpg', img5)
# 第六步:移除背景
aux = removeLight(img4, img5, 1)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('removeLight', aux)
cv2.imwrite('removeLight.jpg', aux)
# 第七步:检测轮廓
output1 = ConnectedComponents(aux)
output2 = ConnectedComponentsStats(aux)
output3 = FindContours(aux)
# 显示并保存图片
cv2.imshow('connectedComponents', output1)
cv2.imwrite('connectedComponents.jpg', output1)
cv2.imshow('connectedComponentsWithStats', output2)
cv2.imwrite('connectedComponentsWithStats.jpg', output2)
cv2.imshow('findContours', output3)
cv2.imwrite('findContours.jpg', output3)
cv2.waitKey(0)1.中值滤波
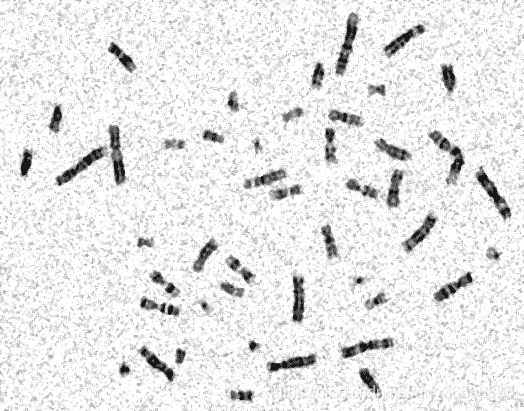
2.图像二值化
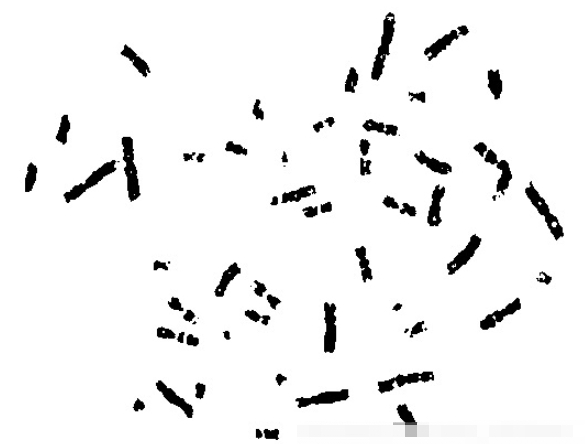

3.膨胀图像

4.腐蚀图像

5.计算光影背景

6.移除背景
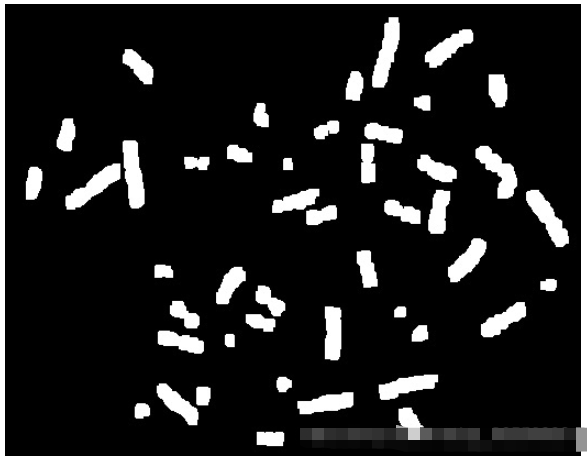
7.检测染色体
(1)connectedComponents.jpg
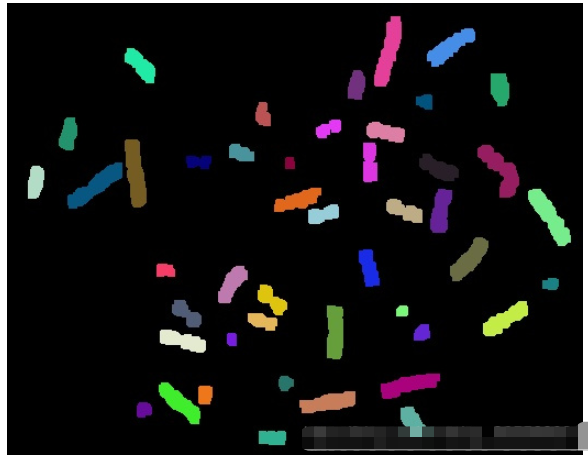
(2)connectedComponentsWithStats.jpg

(3)findContours.jpg
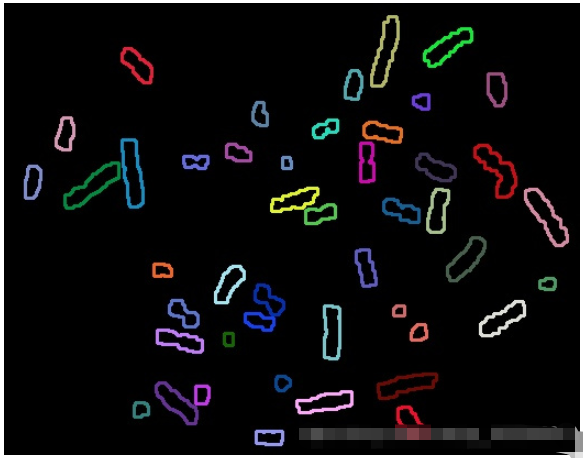
染色体个数为46
到此,相信大家对“Python如何实现数字图像处理染色体计数”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。