本篇文章为大家展示了SpringBoot Security实现前后端分离登录验证,内容简明扼要并且容易理解,绝对能使你眼前一亮,通过这篇文章的详细介绍希望你能有所收获。
第一步,在pom.xml中引入Security配置文件
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency>
第二步,增加Configuration配置文件
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.DisabledException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
/**
* 参考网址:
* https://blog.csdn.net/XlxfyzsFdblj/article/details/82083443
* https://blog.csdn.net/lizc_lizc/article/details/84059004
* https://blog.csdn.net/XlxfyzsFdblj/article/details/82084183
* https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36451151/article/details/83868891
* 查找了很多文件,有用的还有有的,感谢他们的辛勤付出
* Security配置文件,项目启动时就加载了
* @author 程就人生
*
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyPasswordEncoder myPasswordEncoder;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService myCustomUserService;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider())
.httpBasic()
//未登录时,进行json格式的提示,很喜欢这种写法,不用单独写一个又一个的类
.authenticationEntryPoint((request,response,authException) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",403);
map.put("message","未登录");
out.write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
})
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated() //必须授权才能范围
.and()
.formLogin() //使用自带的登录
.permitAll()
//登录失败,返回json
.failureHandler((request,response,ex) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",401);
if (ex instanceof UsernameNotFoundException || ex instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
map.put("message","用户名或密码错误");
} else if (ex instanceof DisabledException) {
map.put("message","账户被禁用");
} else {
map.put("message","登录失败!");
}
out.write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
})
//登录成功,返回json
.successHandler((request,response,authentication) -> {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",200);
map.put("message","登录成功");
map.put("data",authentication);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
})
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
//没有权限,返回json
.accessDeniedHandler((request,response,ex) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",403);
map.put("message", "权限不足");
out.write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
})
.and()
.logout()
//退出成功,返回json
.logoutSuccessHandler((request,response,authentication) -> {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",200);
map.put("message","退出成功");
map.put("data",authentication);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
})
.permitAll();
//开启跨域访问
http.cors().disable();
//开启模拟请求,比如API POST测试工具的测试,不开启时,API POST为报403错误
http.csrf().disable();
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) {
//对于在header里面增加token等类似情况,放行所有OPTIONS请求。
web.ignoring().antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**");
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
//对默认的UserDetailsService进行覆盖
authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(myCustomUserService);
authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(myPasswordEncoder);
return authenticationProvider;
}
}第三步,实现UserDetailsService接口
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 登录专用类
* 自定义类,实现了UserDetailsService接口,用户登录时调用的第一类
* @author 程就人生
*
*/
@Component
public class MyCustomUserService implements UserDetailsService {
/**
* 登陆验证时,通过username获取用户的所有权限信息
* 并返回UserDetails放到spring的全局缓存SecurityContextHolder中,以供授权器使用
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//在这里可以自己调用数据库,对username进行查询,看看在数据库中是否存在
MyUserDetails myUserDetail = new MyUserDetails();
myUserDetail.setUsername(username);
myUserDetail.setPassword("123456");
return myUserDetail;
}
}说明:这个类,主要是用来接收登录传递过来的用户名,然后可以在这里扩展,查询该用户名在数据库中是否存在,不存在时,可以抛出异常。本测试为了演示,把数据写死了。
第四步,实现PasswordEncoder接口
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 自定义的密码加密方法,实现了PasswordEncoder接口
* @author 程就人生
*
*/
@Component
public class MyPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder {
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence charSequence) {
//加密方法可以根据自己的需要修改
return charSequence.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence charSequence, String s) {
return encode(charSequence).equals(s);
}
}说明:这个类主要是对密码加密的处理,以及用户传递过来的密码和数据库密码(UserDetailsService中的密码)进行比对。
第五步,实现UserDetails接口
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 实现了UserDetails接口,只留必需的属性,也可添加自己需要的属性
* @author 程就人生
*
*/
@Component
public class MyUserDetails implements UserDetails {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//登录用户名
private String username;
//登录密码
private String password;
private Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities;
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAuthorities(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this.authorities = authorities;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return this.authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}说明:这个类是用来存储登录成功后的用户数据,登录成功后,可以使用下列代码获取:
MyUserDetails myUserDetails= (MyUserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() .getPrincipal();
代码写完了,接下来需要测试一下,经过测试才能证明代码的有效性,先用浏览器吧。
第一步测试,未登录前访问index,页面直接重定向到默认的login页面了,测试接口OK。
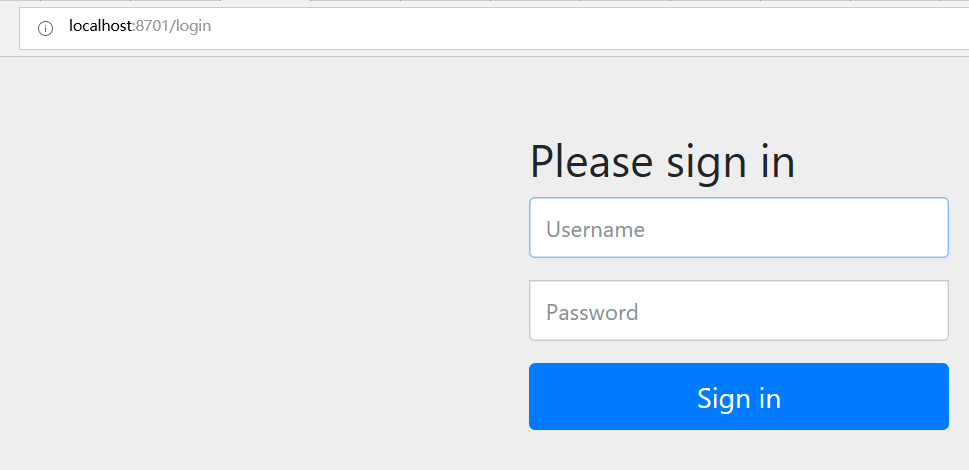
图-1
第二步测试,登录login后,返回了json数据,测试结果OK。

图-2
第三步测试,访问index,返回输出的登录数据,测试结果OK。
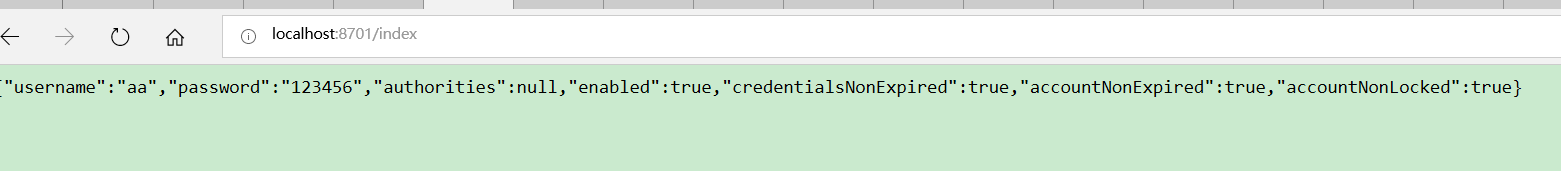
图-3
第四步,访问logout,返回json数据,测试接口OK。

图-4
第五步,用API POST测试,用这个工具模拟ajax请求,看请求结果如何,首先访问index,这个必须登录后才能访问。测试结果ok,返回了我们需要的JSON格式数据。
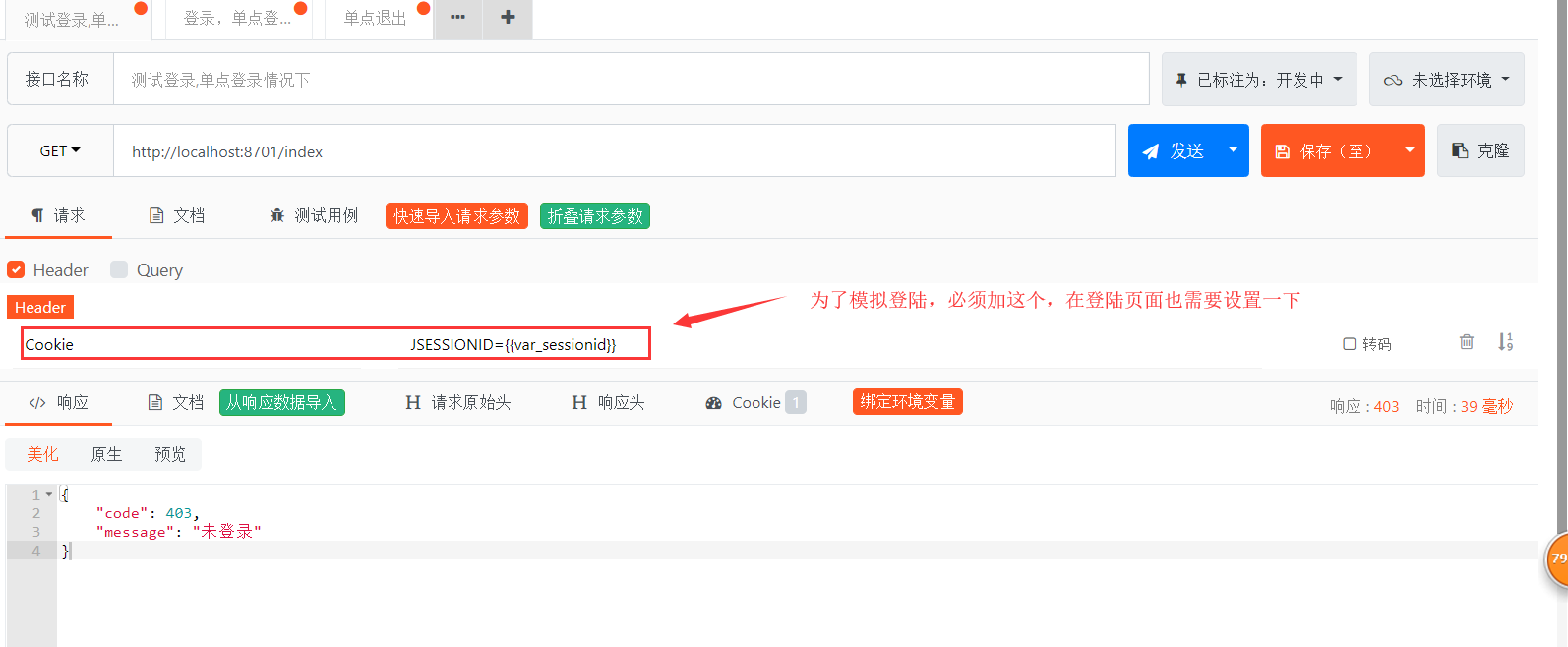
图-5
第六步,在登录模拟对话框,设置环境变量,以保持登录状态。
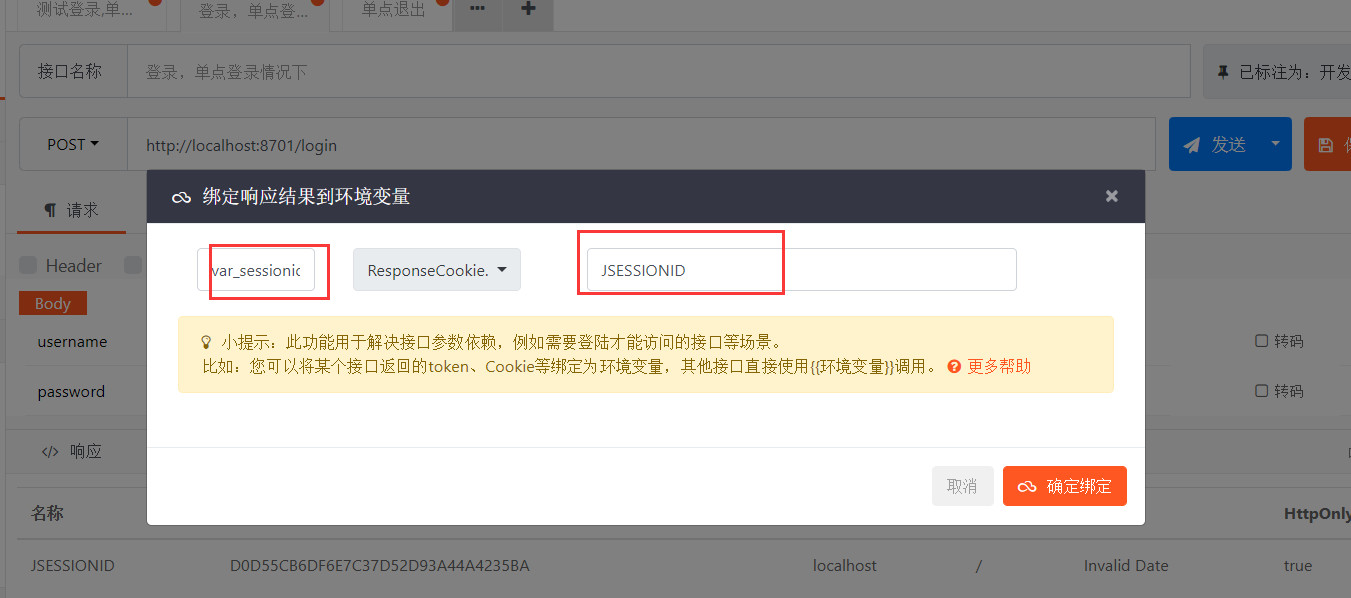
图-6
**第七步,登录测试,返回JSON格式的数据,测试结果OK。
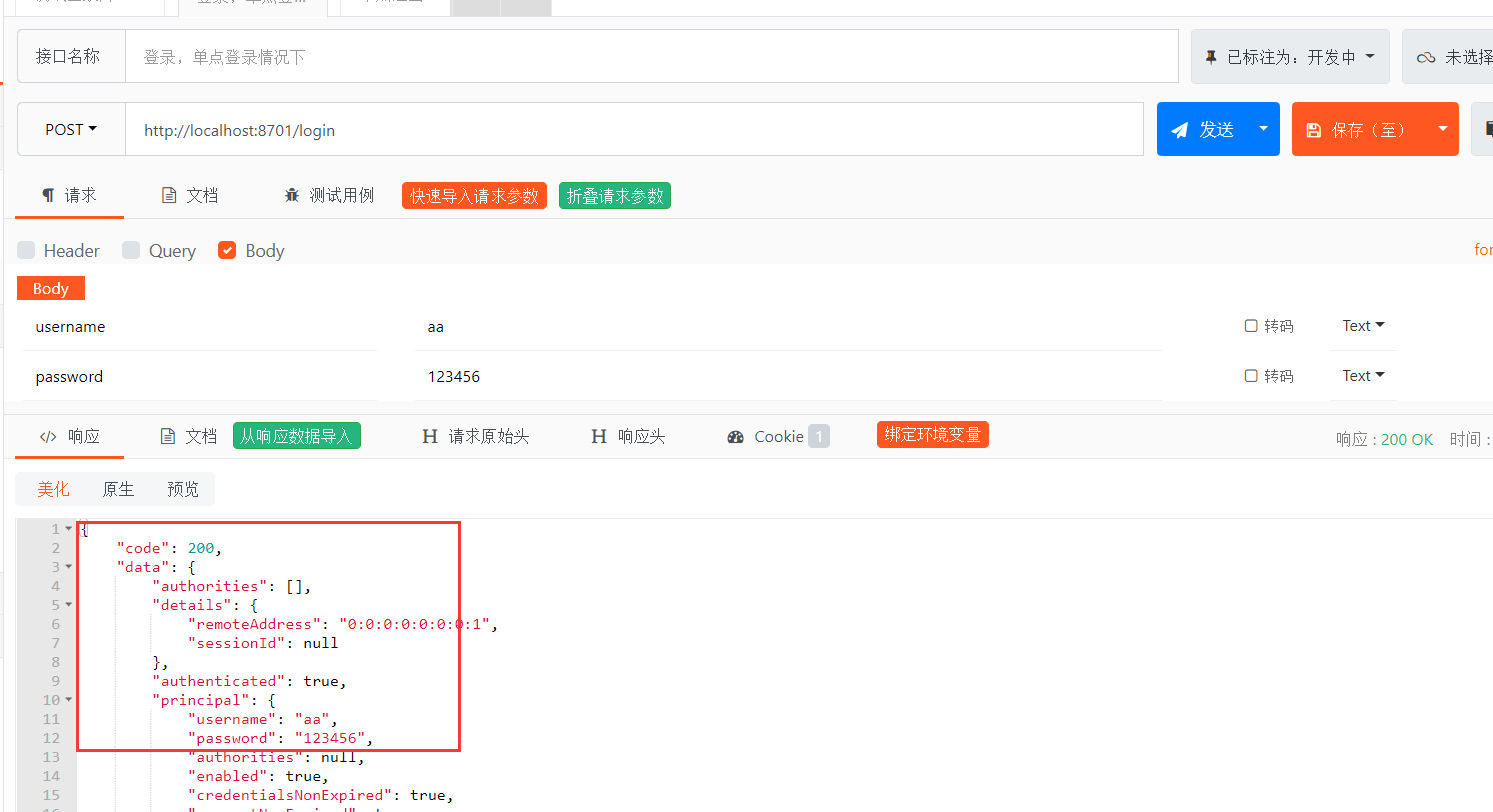
图-7
第八步,在返回到index测试窗口,发送请求,返回当前用户JSON格式的信息,测试结果OK。
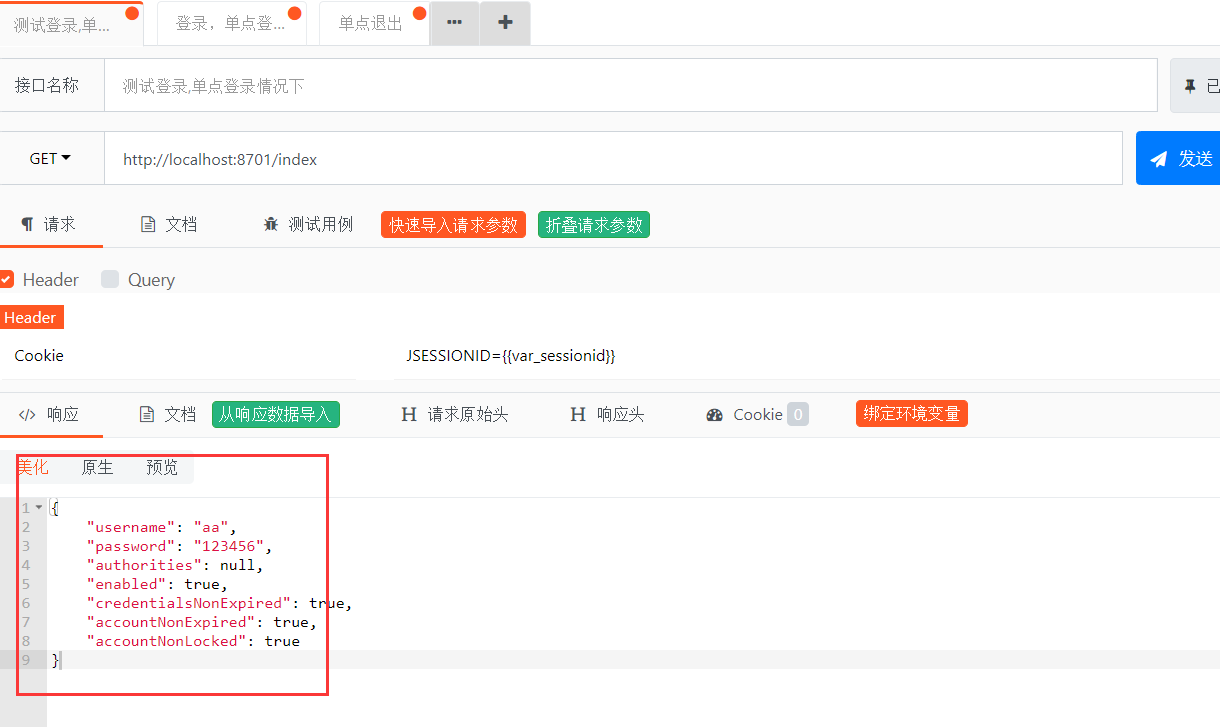
图-8
第九步,测试退出,返回JSON格式数据,测试结果OK
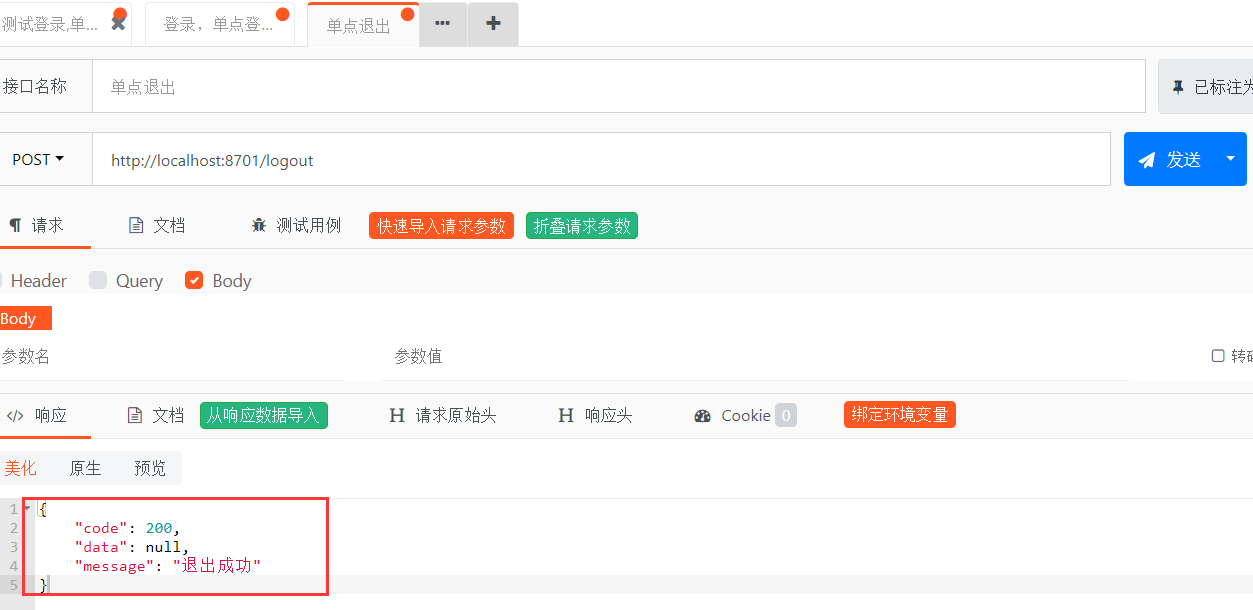
图-9
第十步,退出后,再访问index,出现问题,登录信息还在,LOOK!
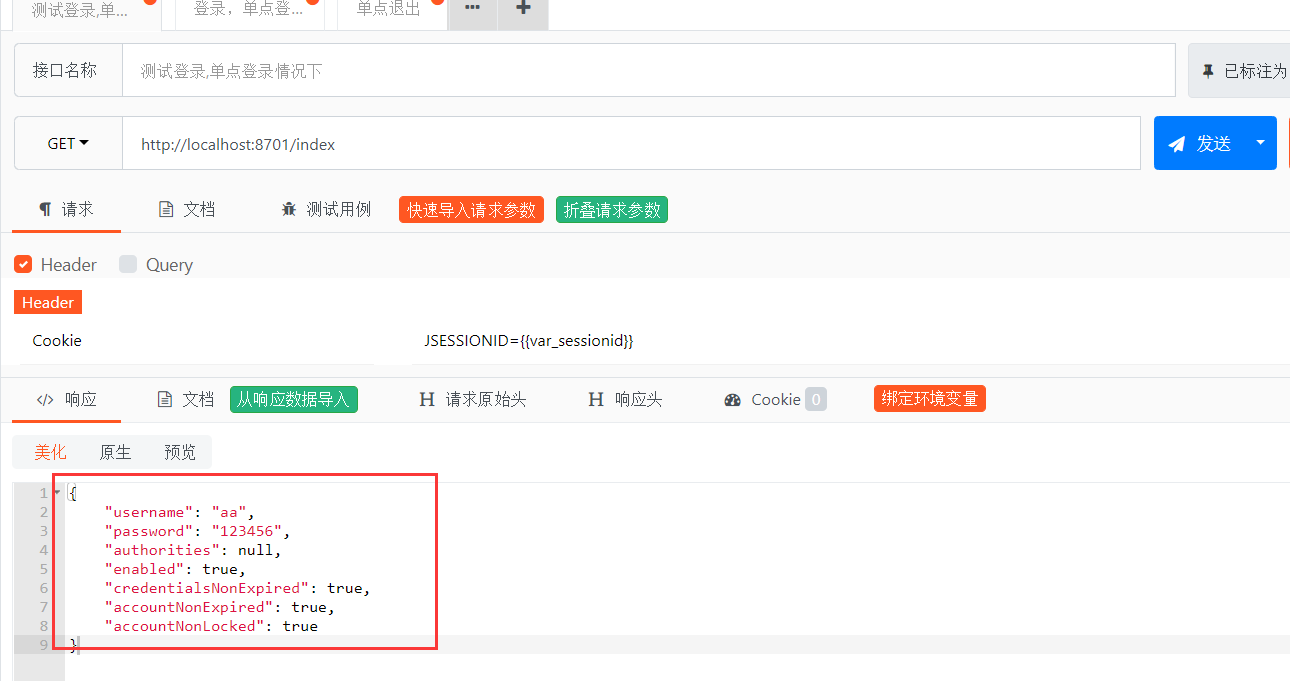
图-10
把头部的header前面的勾去掉,也就是去掉cookie,这时正常了,原因很简单,在退出时,没有清除cookie,这个只能到正式的环境上去测了。API POST再怎么模拟还是和正式环境有区别的。
如果在API POST测试报403错误,那就需要把configuration配置文件里的
//开启跨域访问 http.cors().disable(); //开启模拟请求,比如API POST测试工具的测试,不开启时,API POST为报403错误 http.csrf().disable();
到此这篇关于SpringBoot Security前后端分离登录验证的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot Security登录验证内容请搜索亿速云以前的文章或继续浏
上述内容就是SpringBoot Security实现前后端分离登录验证,你们学到知识或技能了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或者丰富自己的知识储备,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。