本篇内容主要讲解“如何使用JS函数式编程Reduce与Map”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“如何使用JS函数式编程Reduce与Map”吧!
JavaScript是当今流行语言中对函数式编程支持最好的编程语言。函数式编程的七个函数分别为:
- reduce() and reduceRight() to apply an operation to a whole array, reducing it to a single result - map() to transform one array into another by applying a function to each of its elements - flat() to make a single array out of an array of arrays - flatMap() to mix together mapping and flattening - forEach() to simplify writing loops by abstracting the necessary looping code
以及 search 与 selection 的函数:
- filter() to pick some elements from an array - find() and findIndex() to search for elements that satisfy a condition - A pair of predicates, every() and some(), to check an array for a Boolean test
一、array.reduce() 将数列降维至一个值
当我们处理array的时候,总是陷入到无穷尽的loop循环之中,掉入进琐碎的陷阱,戕害我们的思维和大脑。
reduce的基本工作原理如下:
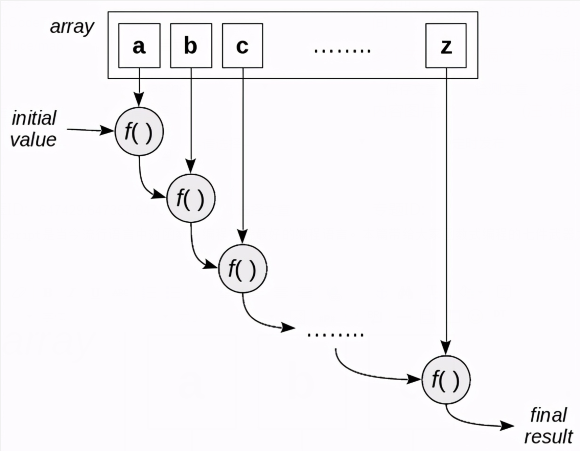
求数列的和
首先从耳熟能详的求数列之和起步。
const myArray = [22, 9, 60, 12, 4, 56]; const sum = (x, y) => x + y; const mySum = myArray.reduce(sum, 0); // 163
观察其运行轨迹:
#+begin_src js :results output const myArray = [22, 9, 60, 12, 4, 56]; const sumAndLog = (x, y) => { console.log(`${x}+${y}=${x + y}`); return x + y; }; myArray.reduce(sumAndLog, 0); #+end_src #+RESULTS: : 0+22=22 : 22+9=31 : 31+60=91 : 91+12=103 : 103+4=107 : 107+56=163求均值
有了reduce,我们得以用“描述”的方式,以decalratively的方式求得average:
const average = arr => arr.reduce(sum, 0) / arr.length; console.log(average(myArray)); // 27.166667
求均值的第二种方法,将length写到里面:
const average2 = (sum, val, ind, arr) => { sum += val; return ind === arr.length - 1 ? sum / arr.length : sum; //将这作为思考的原材料 }; console.log(myArray.reduce(average2, 0)); // 27.166667s更近一步,将average作为固有属性:
Array.prototype.average = function() { return this.reduce((x, y) => x + y, 0) / this.length; }; let myAvg = [22, 9, 60, 12, 4, 56].average(); // 27.166667单词计算多个值
虽然 reduce 只能返回单个结果,但是此返回结果却可以包含多个元素,比如是object。
const average3 = arr => { const sumCount = arr.reduce( (accum, value) => ({sum: value + accum.sum, count: accum.count + 1}), {sum: 0, count: 0} ); return sumCount.sum / sumCount.count; }; console.log(average3([7, 11, 19, 23]));以array的方式改写:
const average4 = arr => { const sumCount = arr.reduce( (accum, value) => [accum[0] + value, xaccum[1] + 1], [0, 0] ); return sumCount[0] / sumCount[1]; }; console.log(average4(myArray)); // 27.166667从右往左的折叠
工作原理如下图:
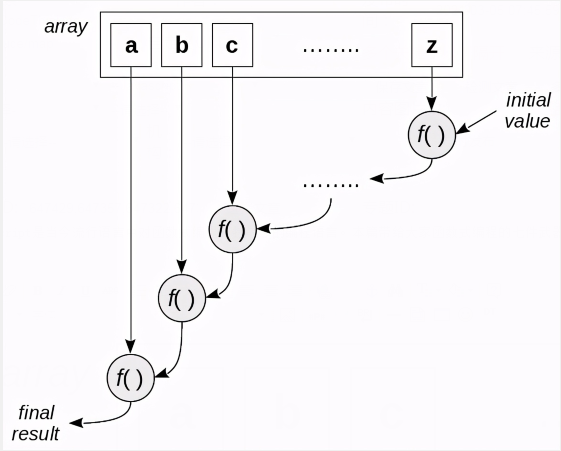
比如 reverse 字符串的常规解决方案为:
const reverseString = str => { let arr = str.split(""); arr.reverse(); return arr.join(""); }; console.log(reverseString("MONTEVIDEO")); // OEDIVETNOM而reduceRight的解题方案呢,
const reverseString2 = str => str.split("").reduceRight((x, y) => x + y, ""); console.log(reverseString2("OEDIVETNOM")); // MONTEVID二、array.map 从数学到编程
map首先是数学上的概念。
从object中提取数据
const markers = [ {name: "AR", lat: -34.6, lon: -58.4}, {name: "BO", lat: -16.5, lon: -68.1}, {name: "BR", lat: -15.8, lon: -47.9}, {name: "CL", lat: -33.4, lon: -70.7}, {name: "CO", lat: 4.6, lon: -74.0}, {name: "EC", lat: -0.3, lon: -78.6}, {name: "PE", lat: -12.0, lon: -77.0}, {name: "PY", lat: -25.2, lon: -57.5}, {name: "UY", lat: -34.9, lon: -56.2}, {name: "VE", lat: 10.5, lon: -66.9}, ]; let averageLat = average(markers.map(x => x.lat)); // -15.76 let averageLon = average(markers.map(x => x.lon)); // -65.53 // extended array.prototype let averageLat2 = markers.map(x => x.lat).average(); let averageLon2 = markers.map(x => x.lon).average();悄无声息的处理数据
看一个我们想当然的应用:
["123.45", "67.8", "90"].map(parseFloat); // [123.45, 67.8, 90] ["123.45", "-67.8", "90"].map(parseInt); // [123, NaN, NaN]
这是因为 parseInt 有一个 optional 的参数 radix。
数列的表示方法
现在我们来创建一个 range.
const range = (start, stop) => new Array(stop - start).fill(0).map((v, i) => start + i); // 必须写一个v,也必须写 new let from2To6 = range(2, 7); // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
尝试求乘方:
const range = (start, stop) => new Array(stop - start).fill(0).map((v, i) => start + i); const factorialByRange = n => range(1, n + 1).reduce((x, y) => x * y, 1); factorialByRange(5); // 120 factorialByRange(3);
尝试字母表:
const ALPHABET = range("A".charCodeAt(), "Z".charCodeAt() + 1).map(x => String.fromCharCode(x) ); // ["A", "B", "C", ... "X", "Y", "Z"]用 reduce 构造 map
reduce是所有其他函数的起点,
const myMap = (arr, fn) => arr.reduce((x, y) => x.concat(fn(y)), []);
尝试两种不同的解决方案:
const myArray = [22, 9, 60, 12, 4, 56]; const dup = x => 2 * x; console.log(myArray.map(dup)); // [44, 18, 120, 24, 8, 112] console.log(myMap(myArray, dup)); // [44, 18, 120, 24, 8, 112] console.log(myArray); // [22, 9, 60, 12, 4, 56]
到此,相信大家对“如何使用JS函数式编程Reduce与Map”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。