这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Hadoop中MapReduce常用算法有哪些,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
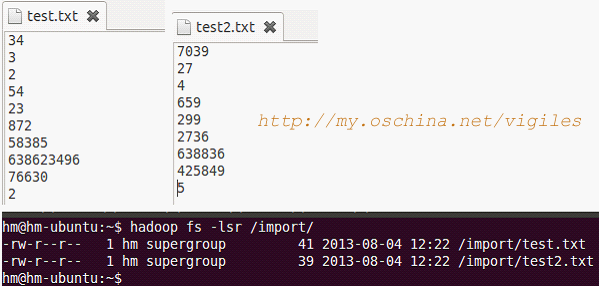
hadoop fs -mkdir /import
创建一个或者多个文本,上传
hadoop fs -put test.txt /import/
package com.cuiweiyou.sort;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
//hadoop默认排序:
//如果k2、v2类型是Text-文本,结果是按照字典顺序
//如果k2、v2类型是LongWritable-数字,结果是按照数字大小顺序
public class SortTest {
/**
* 内部类:映射器 Mapper<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写map方法
*/
public void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这里v1转为k2-数字类型,舍弃k1。null为v2
context.write(new LongWritable(Long.parseLong(v1.toString())), NullWritable.get());
//因为v1可能重复,这时,k2也是可能有重复的
}
}
/**
* 内部类:拆分器 Reducer<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写reduce方法
* 在此方法执行前,有个shuffle过程,会根据k2将对应的v2归并为v2[...]
*/
protected void reduce(LongWritable k2, Iterable<NullWritable> v2, Reducer<LongWritable, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//k2=>k3, v2[...]舍弃。null => v3
context.write(k2, NullWritable.get());
//此时,k3如果发生重复,根据默认算法会发生覆盖,即最终仅保存一个k3
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 声明配置信息
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://localhost:9000");
// 创建作业
Job job = new Job(conf, "SortTest");
job.setJarByClass(SortTest.class);
// 设置mr
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
// 设置输出类型,和Context上下文对象write的参数类型一致
job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
// 设置输入输出路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/import/"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/out"));
// 执行
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
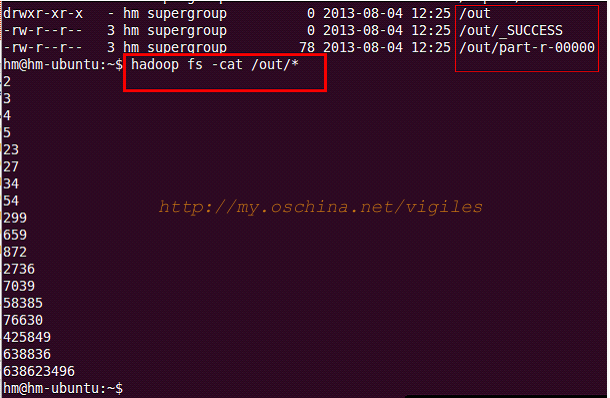
可以看到,不仅排序而且去重了。
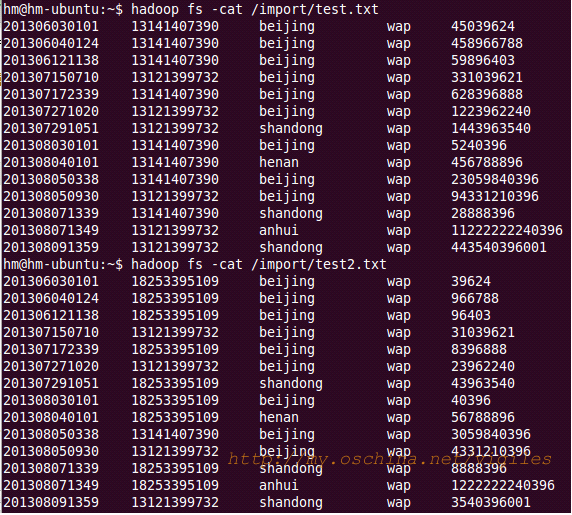
需求:查取手机号有哪些。这里的思路和上面排序算法的思路是一致的,仅仅多了分割出手机号这一步骤。
创建两个文本,手动输入一些测试内容。每个字段用制表符隔开。日期,电话,地址,方式,数据量。
/**
* 映射器 Mapper<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写map方法
*/
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//按照制表符进行分割
String[] tels = v1.toString().split("\t");
//k1 => k2-第2列手机号,null => v2
context.write(new Text(tels[1]), NullWritable.get());
}
}
/************************************************************
* 在map后,reduce前,有个shuffle过程,会根据k2将对应的v2归并为v2[...]
***********************************************************/
/**
* 拆分器 Reducer<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写reduce方法
*/
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<NullWritable> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//此时,k3如果发生重复,根据默认算法会发生覆盖,即最终仅保存一个k3,达到去重到效果
context.write(k2, NullWritable.get());
}
}
// 设置输出类型,和Context上下文对象write的参数类型一致 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
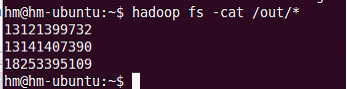
需求:查询在北京地区发生的上网记录。思路同上,当写出 k2 、 v2 时加一个判断即可。
同上。
/**
* 内部类:映射器 Mapper<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写map方法
*/
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//按照制表符进行分割
final String[] adds = v1.toString().split("\t");
//地址在第3列
//k1 => k2-地址,null => v2
if(adds[2].equals("beijing")){
context.write(new Text(v1.toString()), NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
/**
* 内部类:拆分器 Reducer<KEY_IN, VALUE_IN, KEY_OUT, VALUE_OUT>
*/
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
/**
* 重写reduce方法
*/
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<NullWritable> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
context.write(k2, NullWritable.get());
}
}
// 设置输出类型,和Context上下文对象write的参数类型一致 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
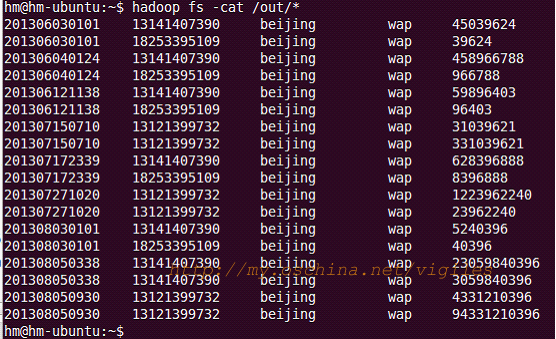
这个算法非常经典,面试必问。实现这个效果的算法也很多。下面是个简单的示例。
需求:找到流量最大值;找出前5个最大值。
同上。
//map
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
//首先创建一个临时变量,保存一个可存储的最小值:Long.MIN_VALUE=-9223372036854775808
long temp = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//找出最大值
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//按照制表符进行分割
final String[] flows = v1.toString().split("\t");
//将文本转数值
final long val = Long.parseLong(flows[4]);
//如果v1比临时变量大,则保存v1的值
if(temp<val){
temp = val;
}
}
/** ---此方法在全部的map任务结束后执行一次。这时仅输出临时变量到最大值--- **/
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
context.write(new LongWritable(temp), NullWritable.get());
System.out.println("文件读取完毕");
}
}
//reduce
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
//临时变量
Long temp = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//因为一个文件得到一个最大值,再次将这些值比对,得到最大的
protected void reduce(LongWritable k2, Iterable<NullWritable> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
long long1 = Long.parseLong(k2.toString());
//如果k2比临时变量大,则保存k2的值
if(temp<long1){
temp = long1;
}
}
/** !!!此方法在全部的reduce任务结束后执行一次。这时仅输出临时变量到最大值!!! **/
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(new LongWritable(temp), NullWritable.get());
}
}
// 设置输出类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
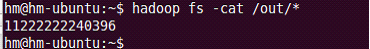
//map
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
//首先创建一个临时变量,保存一个可存储的最小值:Long.MIN_VALUE=-9223372036854775808
long temp = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//Top5存储空间
long[] tops;
/** 次方法在run中调用,在全部map之前执行一次 **/
protected void setup(Context context) {
//初始化数组长度为5
tops = new long[5];
}
//找出最大值
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//按照制表符进行分割
final String[] flows = v1.toString().split("\t");
//将文本转数值
final long val = Long.parseLong(flows[4]);
//保存在0索引
tops[0] = val;
//排序后最大值在最后一个索引,这样从后到前依次减小
Arrays.sort(tops);
}
/** ---此方法在全部到map任务结束后执行一次。这时仅输出临时变量到最大值--- **/
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//保存前5条数据
for( int i = 0; i < tops.length; i++) {
context.write(new LongWritable(tops[i]), NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
//reduce
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable> {
//临时变量
Long temp = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//Top5存储空间
long[] tops;
/** 次方法在run中调用,在全部map之前执行一次 **/
protected void setup(Context context) {
//初始化长度为5
tops = new long[5];
}
//因为每个文件都得到5个值,再次将这些值比对,得到最大的
protected void reduce(LongWritable k2, Iterable<NullWritable> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
long top = Long.parseLong(k2.toString());
//
tops[0] = top;
//
Arrays.sort(tops);
}
/** ---此方法在全部到reduce任务结束后执行一次。输出前5个最大值--- **/
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//保存前5条数据
for( int i = 0; i < tops.length; i++) {
context.write(new LongWritable(tops[i]), NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
// 设置输出类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
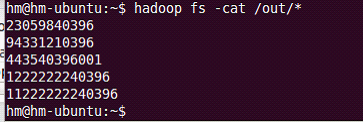
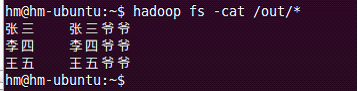
本例中的单表实际就是一个文本文件。
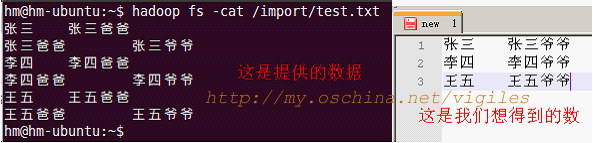
//map
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
//拆分原始数据
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//按制表符拆分记录
String[] splits = v1.toString().split("\t");
//一条k2v2记录:把孙辈作为k2;祖辈加下划线区分,作为v2
context.write(new Text(splits[0]), new Text("_"+splits[1]));
//一条k2v2记录:把祖辈作为k2;孙辈作为v2。就是把原两个单词调换位置保存
context.write(new Text(splits[1]), new Text(splits[0]));
}
/**
张三 _张三爸爸
张三爸爸 张三
张三爸爸 _张三爷爷
张三爷爷 张三爸爸
**/
}
//reduce
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
//拆分k2v2[...]数据
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<Text> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
String grandchild = ""; //孙辈
String grandfather = ""; //祖辈
/**
张三爸爸 [_张三爷爷,张三]
**/
//从迭代中遍历v2[...]
for (Text man : v2) {
String p = man.toString();
//如果单词是以下划线开始的
if(p.startsWith("_")){
//从索引1开始截取字符串,保存到祖辈变量
grandfather = p.substring(1);
}
//如果单词没有下划线起始
else{
//直接赋值给孙辈变量
grandchild = p;
}
}
//在得到有效数据的情况下
if( grandchild!="" && grandfather!=""){
//写出得到的结果。
context.write(new Text(grandchild), new Text(grandfather));
}
/**
k3=张三,v3=张三爷爷
**/
}
}
// 设置输出类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
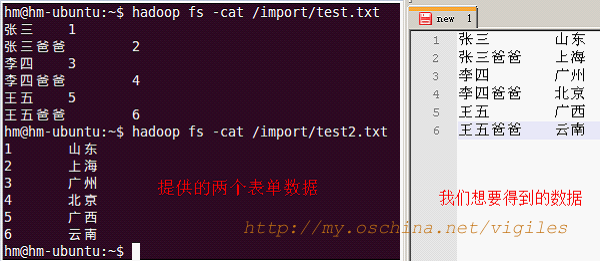
本例中仍简单采用两个文本文件。
//map
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
//拆分原始数据
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
//拆分记录
String[] splited = v1.toString().split("\t");
//如果第一列是数字(使用正则判断),就是地址表
if(splited[0].matches("^[-+]?(([0-9]+)([.]([0-9]+))?|([.]([0-9]+))?)$")){
String addreId = splited[0];
String address = splited[1];
//k2,v2-加两条下划线作为前缀标识为地址
context.write(new Text(addreId), new Text("__"+address));
}
//否则就是人员表
else{
String personId = splited[1];
String persName = splited[0];
//k2,v2-加两条横线作为前缀标识为人员
context.write(new Text(personId), new Text("--"+persName));
}
/**
1 __北京
1 --张三
**/
}
}
//reduce
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
//拆分k2v2[...]数据
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<Text> v2, Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
String address = ""; //地址
String person = ""; //人员
/**
1, [__北京,--张三]
**/
//迭代的是address或者person
for (Text text : v2) {
String tmp = text.toString();
if(tmp.startsWith("__")){
//如果是__开头的是address
address = tmp.substring(2); //从索引2开始截取字符串
}
if(tmp.startsWith("--")){
//如果是--开头的是person
person = tmp.substring(2);
}
}
context.write(new Text(person), new Text(address));
}
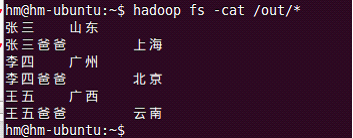
/**
k3=张三,v3=北京
**/
// 设置输出类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
关于“Hadoop中MapReduce常用算法有哪些”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。